Cloud Communication - Accessing Variables
Cloud Communication
Review: What is the Cloud?
Internet of Things
- Things
- “smart” devices that are programmed interact with environment
- Internet
- connect to the internet to send and receive data
IoT Cloud Platforms
- Various services that allow you to enhance your device with internet capability
Examples of IoT Cloud Services
- Update device code and firmware
- Receive status messages (like we do with Serial monitor)
- Read the values of variables
- Control device / execute function calls
- Store data from device (e.g. the hourly temperature for the past 6 months)
- Run analytics (e.g. how often does one of my 4,000 device fail)
- Manage device with publicly-accessible web/mobile
IoT Cloud Platform Companies
- Very competitive and growth space
- Established firms: Google Cloud IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT, Amazon Web Services
- Startups: Particle, Losant, Ubidots, Initial State, Tinamous
- Various: Thingspeak (supports MATLAB), IFTTT
Particle Cloud Features
- Update device code and firmware
- Receive status messages (like we do with Serial monitor)
- Read the values of variables
- Control device / execute function calls
Particle Cloud Does NOT
- Store data from device
- Ex. the hourly temperature for the past 6 months)
- Run analytics
- Ex. how often does one of my 4,000 device fail)
- Manage device with publicly-accessible web/mobile
Particle Cloud
- Photon 2 has built in support for connecting to Particle Cloud
- Particle Cloud is essentially free (very generous free tier)
- Basically acts as a real-time communication system
- i.e. the current temperature, but not temperature from last Tuesday
- For data storage and analysis, we will use a different service later in the course
Quick Note
- All the features we will discuss are not unique to Particle Cloud
- It is possible to read variables and execute functions from most companies’ platforms
- The syntax and mechanisms will vary from Particle Cloud, but the concepts are transferable
Key operations in Particle Cloud
- Accessing data (cloud variables)
- Control device (cloud functions)
- Publishing (events part 1)
- Subscribing (events part 2)
Cloud Variables
- Register / expose a variable in your Photon 2 code so it can be accessed online
- This does not publish the value of the variable automatically
- Cloud is notified variable exists, and it is retrieved only when requested
- Up to 20 variables may be registered
Cloud Variables Process
- Declare global variable (must be
int,double,String,bool) - Call
Particle.variablewithinsetup()to register the variable
Cloud Variable Syntax
Particle.variable(<<REGISTERED_NAME>>, <<ACTUAL_VARIABLE>>);
Example
double f; //declare global variable
String lightValue; //declare global variable
void setup() {
Particle.variable("lightValue", photoSensor); //register variable
Particle.variable("tempFahr", f); //register variable
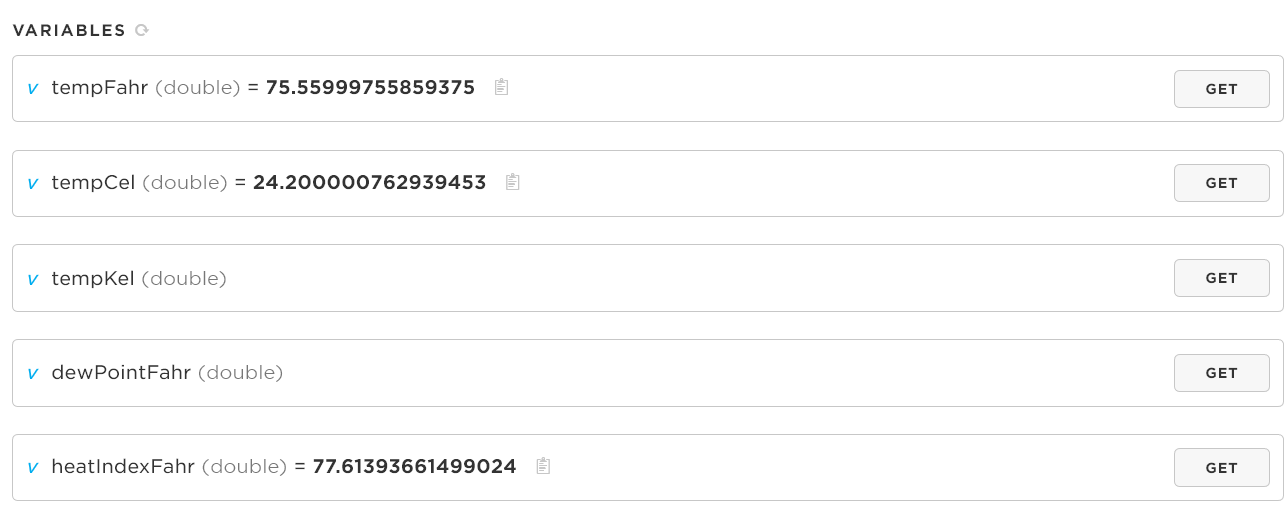
Accessing Cloud Variables - Particle Console
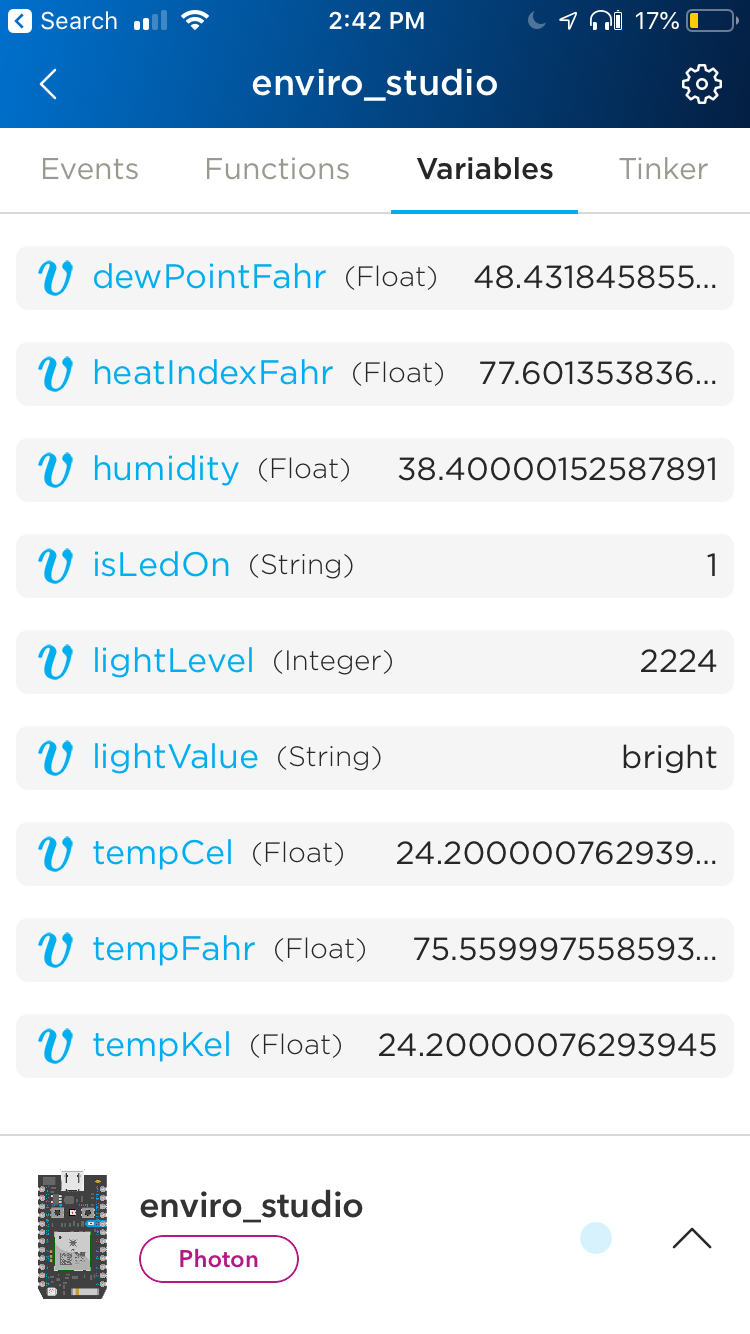
Accessing Cloud Variables - App
Accessing Cloud Variables - REST
-
Variables can be accessed by any device or service via REST
-
REST is very common protocol for sharing data across the internet
-
REST call syntax
GET /v1/devices/{DEVICE_ID}/{VARIABLE}
Lab
- Create cloud variables for both photoresistor value and light level (dark, ambient, bright)