DHT20 - Temperature and Humidity Sensor
DHT20 - Temperature and Humidity Sensor
Sensor Type
Important! There are different styles of DHT sensors, and they need to be connected and programmed differently. Make sure to verify which sensor you have before proceding.
Digital Temperature and Humidity Sensor
- DHT 20 measure temperature and relative humidity
- Unlike TMP36, this has a digital interface and no calculation or conversion is needed
Wiring Guide - 4 Pins
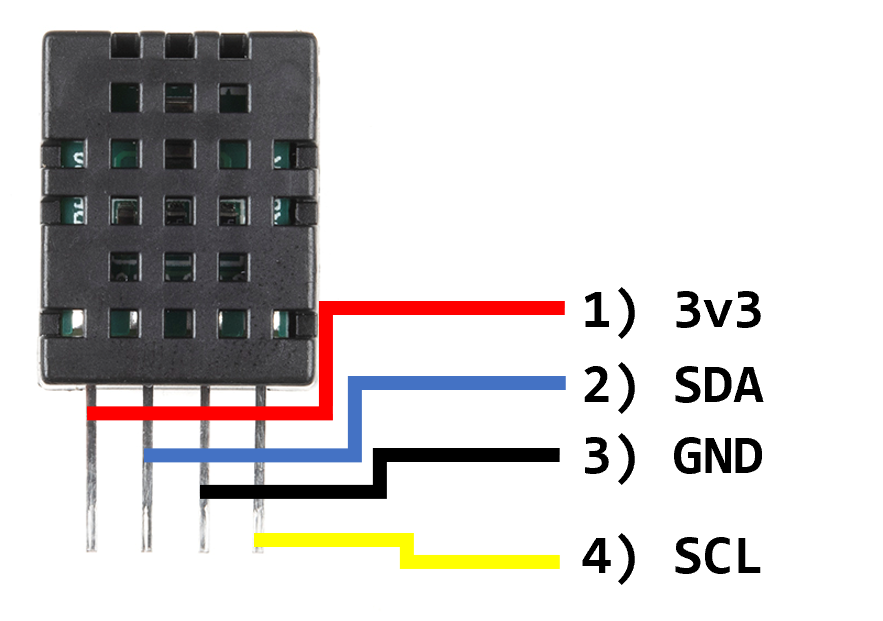
- 3.3V
- SDA
- Ground
- SCL
Wiring

Note: In Fritzing, if you don’t find a DHT 20 (black), you can used the DHT 22 or DHT 11 in your diagram.
Software Library
- The DHT20 uses a protocol called I2C to send data
- In order to communicate with the device, we will need to use a special library
- The Photon 2-compatible library we will use is:
DHT_I2C_Particle
Library Setup
#include "DHT20.h"
DHT20 DHT;
setup()
//initialize DHT software object
dht.begin();
Wait for Data and Error Checking
int status = dht.read();
if (status == DHT20_OK) { // means this was valid read
//proceed with processing sensor values
}
Reading Values
// Read humidity
float h = dht.getHumidity();
// Read temperature as Celsius
float t = dht.getTemperature();
// Read temperature as Farenheit
float f = dht.getTemperatureF();
Full Example
//
// FILE: DHT20_simple.ino
// AUTHOR: Rob Parke based on work by Rob Tillaart
// PURPOSE: Demo for DHT20 I2C humidity & temperature sensor
//
// Always check datasheet - front view
//
// +--------------+
// VDD ----| 1 |
// SDA ----| 2 DHT20 |
// GND ----| 3 |
// SCL ----| 4 |
// +--------------+
#include "DHT20.h"
DHT20 dht;
void setup() {
dht.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
int status = dht.read();
if (status == DHT20_OK) { // valid read
Serial.print("DHT20 \t");
Serial.print("% Humidity: " + String(dht.getHumidity()));
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(String(dht.getTemperature()) + " C");
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(String(dht.getTemperatureF()) + " F");
} else {
Serial.println("Invalid read");
}
delay(1000);
}
Notes
- Always wait about 2.5 seconds in between measurements (use
millispreferably for this instead ofdelay)