Reading Resistor Bands
Resistors Bands
Accessibility Note
- Resistor values are determined visually by color bands
- Unfortunately resistor labeling is not accessibly designed
- To support students who are color blind or have difficulty distinguishing colors, here are resources for support
Resistor Labels
- The color codes indicate the resistance in Ohms (and sometimes how precise they are)
- There are 4 bands (colors), 5 band, and 6 band resistors
- Four band resistors are the most common, and the ones we will encounter in this class
Resistor Chart
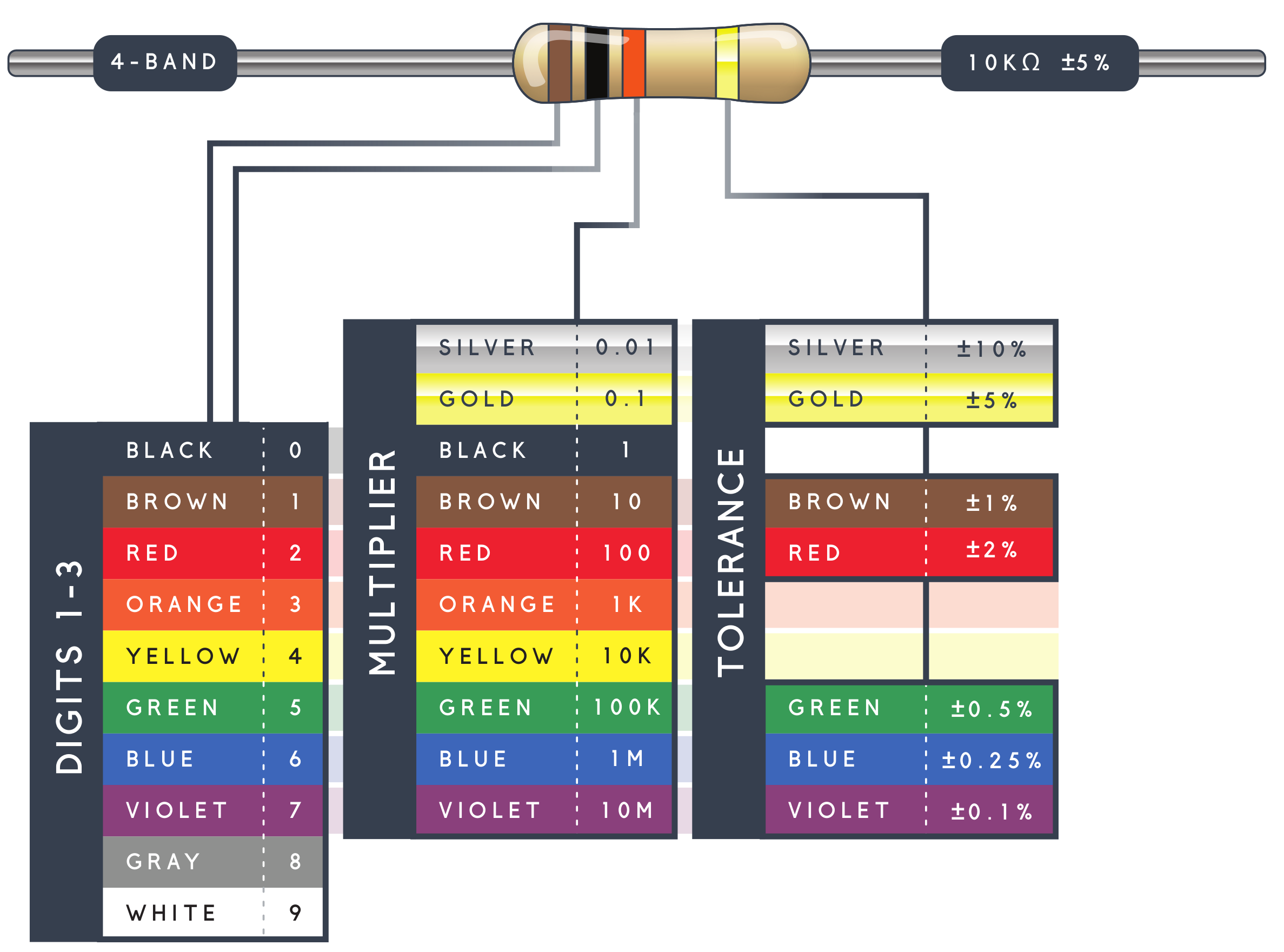
Understanding Resistor Chart

- Align such that the group of three bands are on the left
- The first two bands are the digits
- The third band is the multiplier (a power of ten)
- The last band is the tolerance (acceptable range of Ohms)
- Nominal value (Ohms) use SI units: Ohm, K Ohms (1,000 Ohms), or M Ohms (1,000,000 Ohms)
Reading Bands Ex. 1
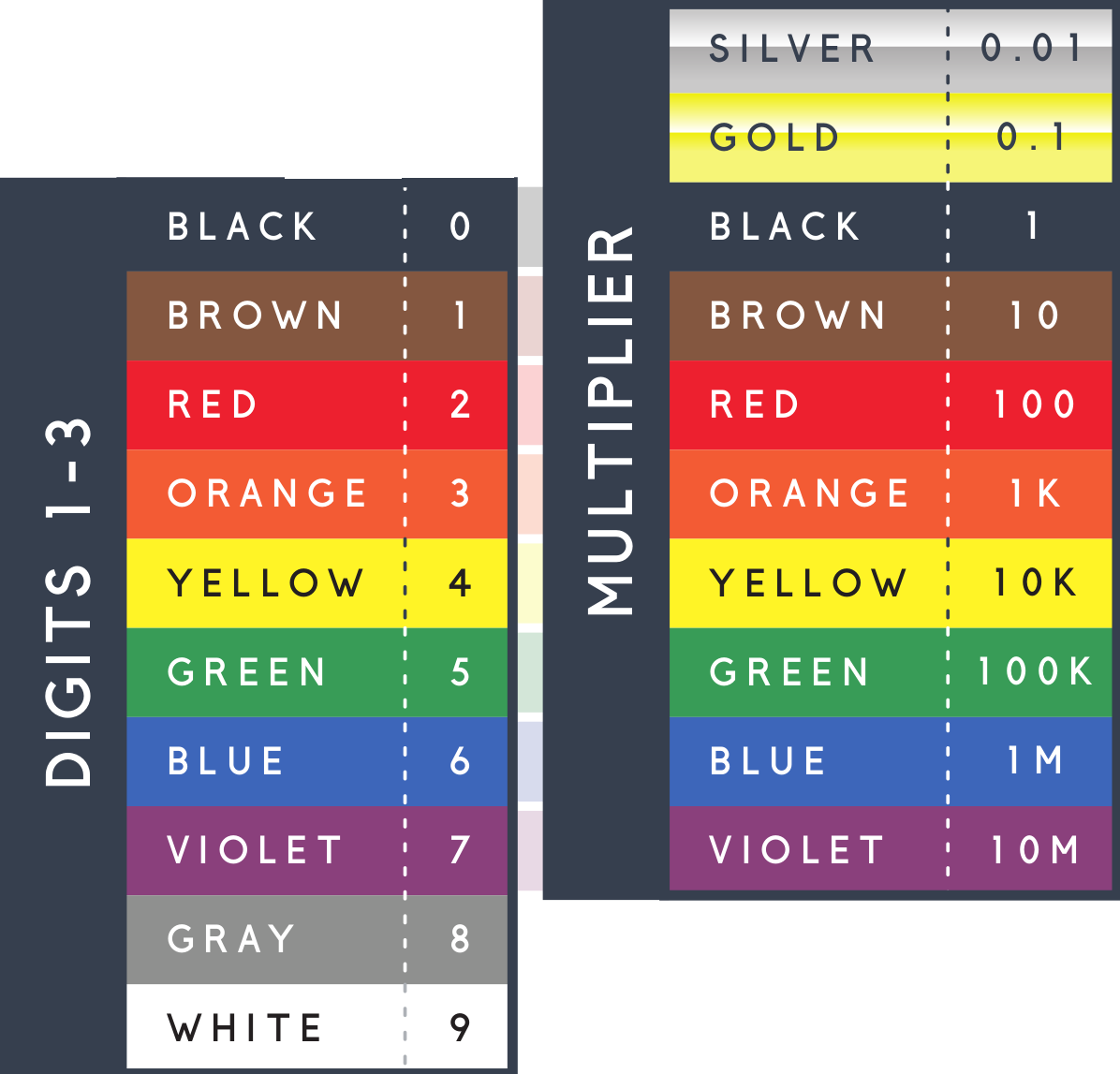 |
 |
1. Orange 2. Orange 3. Brown 4. Gold |
Reading Bands Ex. 1
 |
 |
1. Orange = 3 2. Orange = 3 3. Brown = 10 (10^1) 4. Gold +-5% |
Reading Bands Ex. 1
- Orange Orange Brown ==> 3 3 10 (or 10^1)
- 33 * 10 = 330 Ohms
Reading Bands Ex. 2
 |
 |
1. Gray 2. White 3. Yellow 4. Gold |
Reading Bands Ex. 2
 |
 |
1. Gray = 8 2. White = 9 3. Yellow = 4 4. Gold +-5% |
Reading Bands Ex. 2
- Gray White Yellow ==> 8 9 10000 (or 10^4)
- 89 * 10000 = 890000 Ohms
- But! Since this is over 1000 Ohms, we should use K Ohms (1000 Ohms)
- 890000 = 890 * 1000 = 890 K Ohms
##
| | |
| ———————————————————— | ———————————————————— |
| 1. 2.
2.
3. 4.
4. |
|  |
|