Multi Tasking
Multi-Tasking: Delay
First, a Clarification
- We’ve learned about creating a button / latch toggle
int currButtonVal = digitalRead(PIN_BUTTON); if (currButtonVal == LOW && prevButtonVal == HIGH) { // code to execute on button press goes here } prevButtonVal = currButtonVal; - Latches allow us to react to single button presses
- Multi-tasking code is solving a different problem
Consider

What is your phone doing right now while you’re not using it?
Review: Basic LED Blink
void setup() {
pinMode(D7, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(D7, HIGH);
delay(1000); //what is happening during the 1 sec delay?
digitalWrite(D7, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
Questions
- How do we get two LEDs to each blink on/off at 1 sec intervals?
- How do we get one LEDs to blink on/off at 1 sec interval, and the second LED to blink at 2 sec intervals?
- How do we get one LEDs to blink on/off at 1.442 sec interval, and the second LED to blink at 3.83 sec intervals?
Delay Problems
delay()is blocking- This means the Photon 2 is essentially paused and can’t do anything else
- We need to be able to synchronize events and multi-task just like our computers and phones
- This means in the time between the LED turning off and turning on, the Photon 2 can do other things
Step 1: Let’s Use the Clock
millis()is a function that returns the “relative current time”- Number of milliseconds that have elapsed since the Photon 2 last turned on / reset
- We can call
millis()at different points in time to compare the passage of time - When a specific time has elapsed, we can take an action
Note about millis() and long
-
The “on” time is returned as an
long -
longis like anintbut has a larger capacity -
Normally
longstores 32 bit numbers (positive and negative) -
range of
long: -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
Note about millis() and unsigned long
-
However, the “on” time will never be negative
-
We can specify a variable as
unsignedwhich means the lowest value is 0 -
range of
unsigned long: 0 to 4,294,967,295 -
Syntax
unsigned long currentTime = millis();
Step 2: Track the Current State
- State represents any variables or relevant data about our device at the current moment
- You decide what states are relevant for your program
- E.g.
AcceptingPayment,ReceivingData,DishesDry,AlarmOff
- E.g.
- For a single LED, the states are either ON (HIGH) or OFF (LOW)
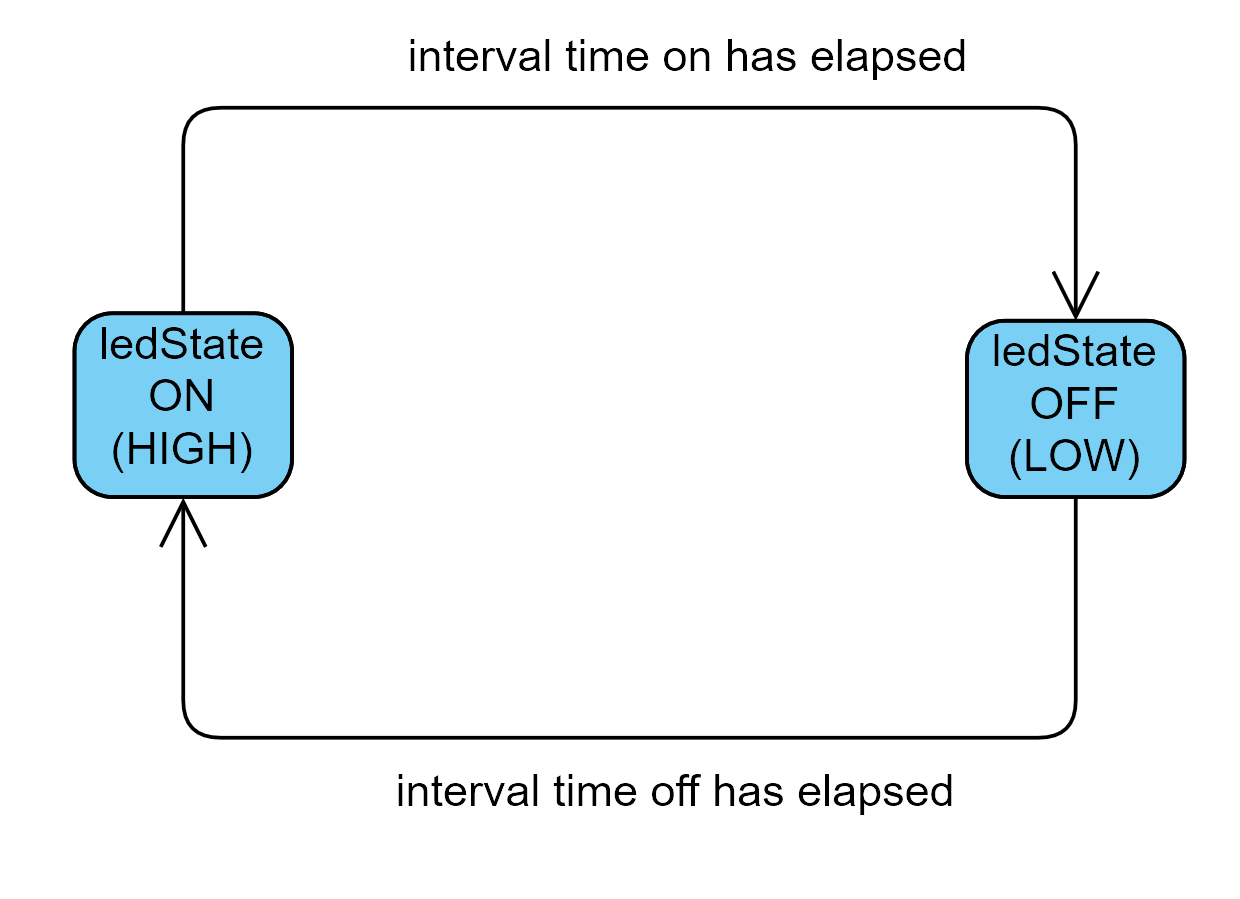
Our New Plan
- if
ledState== LOW AND interval is over- then
ledState= HIGH - update time
- turn on LED
- then
- if
ledState== HIGH AND interval is overledState= LOW- update time
- turn off LED
Visual Representation
Code: Blink LED without Delay
unsigned long prevMillis = 0; //last time we checked time
int ledState = LOW; //initial state
int interval = 300;
void loop() {
unsigned long curMillis = millis(); //current time
//check if (now - previous) is more than our interval
if (curMillis - prevMillis >= interval) {
prevMillis = curMillis; //if YES, update previous
if (ledState == LOW) { //if LED ON, now it is OFF
ledState = HIGH;
} else { //if LED ON, now it is OFF
ledState = LOW;
}
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, ledState);
}
Code: More Concise Blink LED without Delay
unsigned long prevMillis = 0; //last time we checked time
int ledState = LOW; //initial state
int interval = 300;
void loop() {
unsigned long curMillis = millis(); //current time
//check if (now - previous) is more than our interval
if (curMillis - prevMillis >= interval) {
prevMillis = curMillis; //if YES, update previous
ledState = !ledState; //toggle true / false
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, ledState);
}
Lab
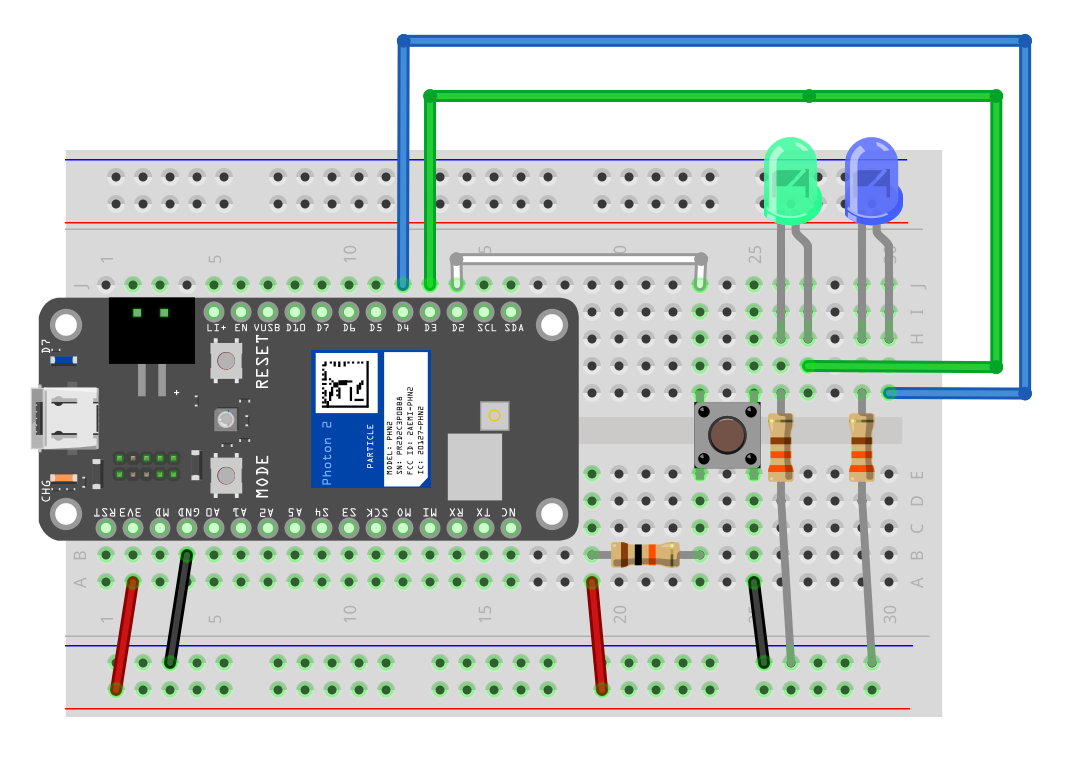
Lab Goals
- Blink LED1 every 300 ms
- Blink LED2 every 146 ms
- Create toggle button (latch) to turn ON BOARD on at rising edge and off again at the rising edge
- Track the number of times the button is pressed
- Publish the number of button presses to cloud every 10000 ms
- Extra Challenge
- Change LED1 to be on for 300 ms and off for 700 ms
- Change code so that when the toggle button is pressed, LED2 starts blinking every 146 milliseconds, and when the toggle button is pressed again, LED2 stops blinking
Stages to Build
- Use
delayto blink LED1 every 300 ms and then check for a button press (not a toggle); display Serial message if button pressed - Use
millis()to fix blocking in #1 (we’ll do #1 and #2 together) - Use
millis()to blink LED2 every 146 ms - Enable toggle button to turn ON BOARD LED on and off on the rising edge
- Track number of button presses and use
millis()to publish number of button presses every 10000 ms
Starting Code
const int PIN_BUTTON = D2;
const int PIN_LED1 = D3;
const int PIN_LED2 = D4;
void setup()
{
pinMode(PIN_BUTTON, INPUT);
pinMode(PIN_LED1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_LED2, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(PIN_LED1, HIGH);
delay(300);
digitalWrite(PIN_LED1, LOW);
delay(300);
digitalWrite(PIN_LED1, HIGH);
delay(300);
digitalWrite(PIN_LED1, LOW);
delay(300);
}