Multimeters
Multimeters
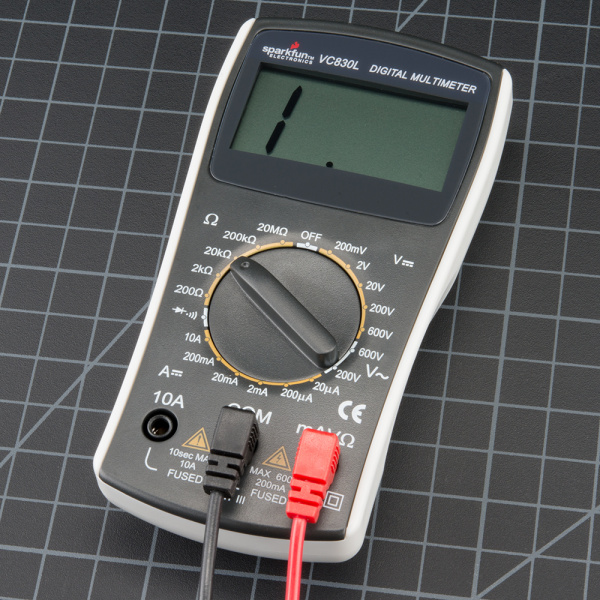

Digital multimeters (DMM)
- Allow you to measure the electrical properties of your circuit
- Measure voltage, resistance, continuity, and current
- Some multimeters can measure capacitance and temperature
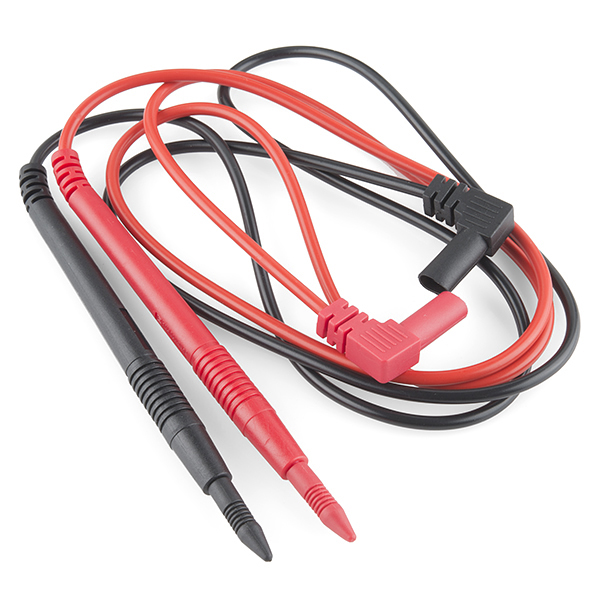


General Multimeter Setup
1) Plug in probes (black goes to common, red goes the appropriate ports)
- For our class, we will be measure milliamps, ohms, and V so use right port 2) Turn knob to appropriate zone 3) Follow specific steps for type of measurement
Setting Multimeter to Measure Resistance

Notes about Measuring Resistance
- Resistance should be measured outside the circuit
- Always remove the resistor before measuring
How to Measure Resistance
1) Remove the resistor from circuit 2) Touch one probe to each end of the resistor 3) Adjust the knob until a valid reading appears
- If meters reads OL, 1, or 0, then adjust the knob
Exercise
- Use multimeter to measure the resistance of your potentiometer
Setting Multimeter to Measure DC Voltage

Notes about Measuring DC Voltage
- Voltage is measured with the circuit is operating with electricity
- Connect the multimeter in parallel with the component you want to measure
How to Measure DC Voltage
1) Touch the black probe to ground 2) Touch the red probe to the place in the circuit you want to measure 3) Adjust the knob until a valid reading appears
- If meters reads OL or 1, adjust the knob
Exercise
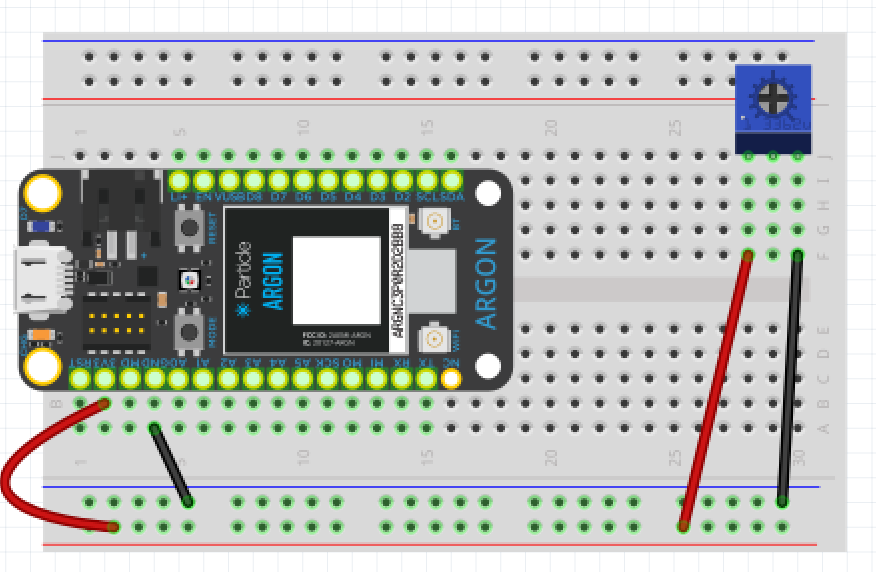
- Connect potentiometer to 3.3v and ground.
- Measure voltage at pin 2 as your turn the knob
Setting Multimeter to Measure Continuity

Notes about Measuring Continuity
- Continuity checks if two points are connected (e.g. if they are connected by a wire)
- When each probe is touching two places that are connected, the multimeter will beep
- Continuity can only be checked when the circuit is off (no electricity)
- Useful to find out if a wire has broken or there is a short circuit somewhere
How to Measure Continuity
1) Touch the black probe to one point in the circuit 2) Touch the red probe to another point in circuit 3) If the multimeter beeps, the two points are connected
- If there is no beep, the points are not connected
Other Uses
- In our class, we will not typically measure current or AC voltage, but these are included for reference
Setting Multimeter to Measure DC Current

Notes about Measuring DC Current
- Current is measured with the circuit is operating with electricity
- Connect the multimeter in series with the component you want to measure
- This means breaking the circuit and inserting the multimeter in line (series) with the circuit
- There are two ports for measuring current depending on amperage
- Our devices have 10 A and 200 mA
How to Measure DC Current
1) “Break” the circuit at the point you want to measure current 2) Touch the black probe to one point of the broken connection 3) Touch the red probe to the other point in circuit
Setting Multimeter to Measure AC Voltage

Notes about Measuring AC Voltage
- AC voltage is dangerous and potentially fatal if mishandled
- While it is possible possible to measure AC voltage with the handheld multimeter, it is safer to use a device called a non-contact tester