Analog vs. Digital
Analog vs. Digital
Questions
- What is an example of something that is analog?
- What is an example of something that is digital?
Analog vs. Digital


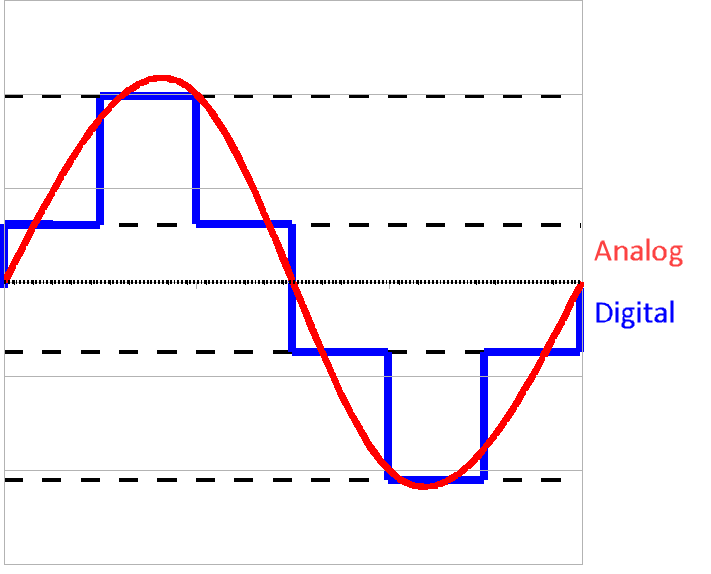
Analog
-
The world is analog!
-
Paints blend smoothly together
-
Violin notes increase smoothly in pitch
-
There are can be infinite variations for these events
Digital
-
Instead of being infinite, digital signals are discrete (or finite)
-
Think binary: the switch is either on or off (not “a little bit on”)
- Digital values often will have more than just two states
- They still have a fixed number of possible values
- Ex: Colors on computers are represented three values (amount of red, green, and blue
- Each R, G, B value can be 0-255
Analog vs. Digital
Review
Setting input / output with pinMode
Syntax
pinMode(PIN_NUMBER, MODE);
//MODE: OUTPUT or INPUT
- Most pins on the Photocan be configured to SEND output (e.g. to turn on a light) or to RECEIVE input (e.g. a button press)
- When you want to use a pin in your program, you should specify its mode in
setup()
Digital Output
- These are signals that are HIGH or LOW
- HIGH / true is 5V (pin VUSB) or 3.3V (pin 3.3v)
- LOW / false is 0V (ground)
- What is an example of digital output we have seen so far?
Writing Digital Output with digitalWrite
Syntax
digitalWrite(PIN_NUMBER, VALUE);
//VALUE: HIGH or LOW
- You can send an ON (HIGH) or OFF (LOW) signal at output on a pin
- This is writing a digital value
- Digital values are like boolean values: 0/1, on/off, true/false