State Machines Part 1 - Overview
State Machines
ITP 348 - Introduction to Physical Computing

Learning Objectives
- Understand what a state machine is
- Describe situations where a state machine is useful
- Analyze a real-world situation to create states, transitions, and input
- Implement a state machine in Photon 2 firmware
What’s the main point?
- Our devices should operate remotely without constant user intervention
- Our devices can receive various sensor data (input) in different situations (states), which results in different actions (outputs)
- Tracking and organizing all these possibilities can become very complicated
- State machines provide a way of thinking about and designing for the various situations that arise
State Machine
- A state machine (or finite state machine) is mental model to help us make decisions
- It is not just hardware or just software code
- Examine
- What has happened previously (state)
- What is happening currently (input)
- Then generate
- Next output
- Next state (transition)
Example #1 Stoplight

Example #1 Stoplight
- Consider a simplified stoplight without any pedestrians
- Lights changed after a fixed time
- What states are there?
- How do we transition to new states?
Example #1 Stoplight Diagram
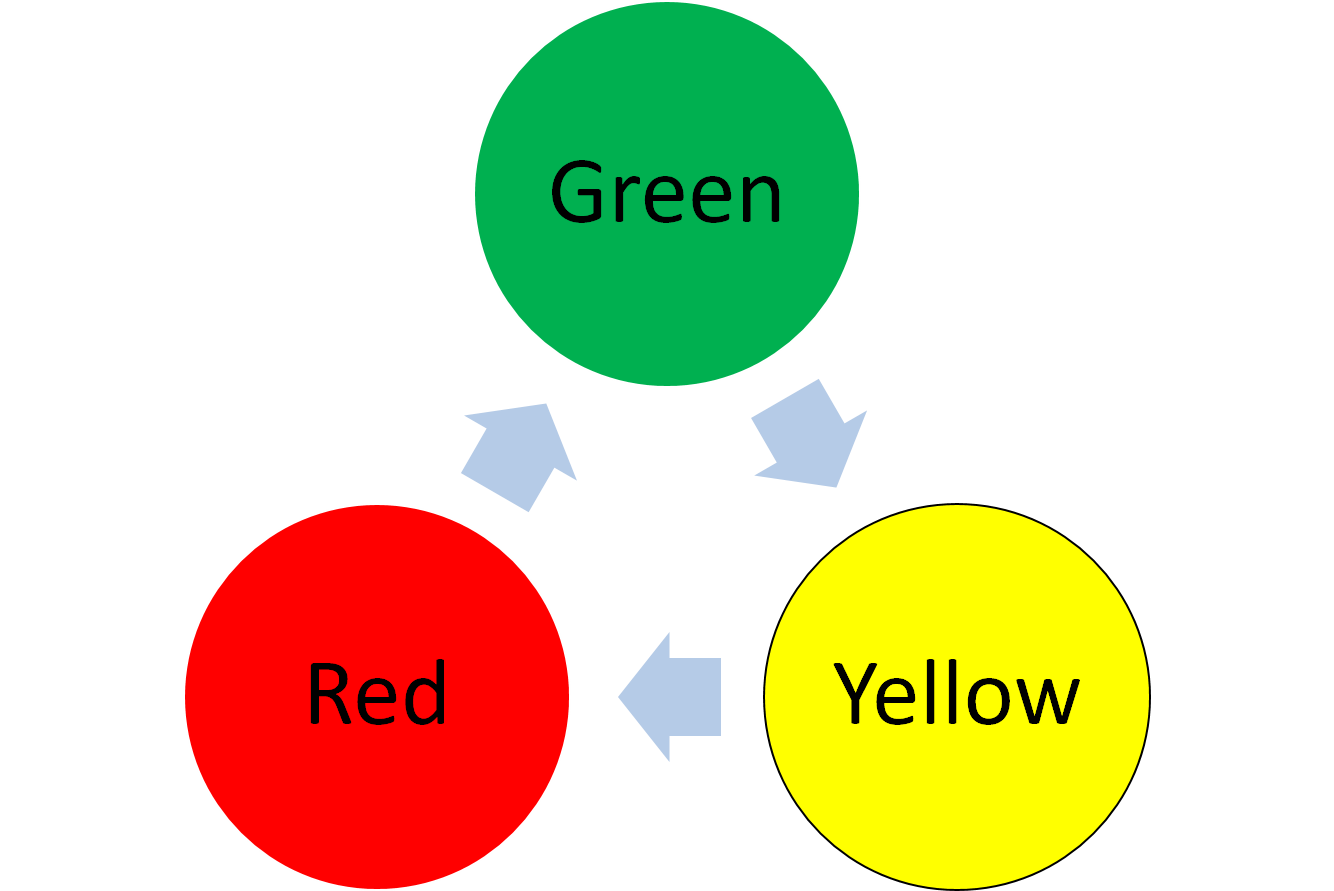
Example #1 Stoplight
| State | Output (Stoplight Color) |
|---|---|
| Traffic Flows | Green |
| Traffic Stopping | Yellow |
| Traffic Stopped | Red |
Example #2 Sprinkles Cupcake ATM

Example #2 Sprinkles Cupcake ATM Diagram
- Similar to soft drink vending machine
- What states are there?
- How do we transition to new states?
Example #2 Sprinkles Cupcake ATM
| State | Input | Next State |
|---|---|---|
| Idle | None | Idle |
| Idle | Start button | Display choices |
| Display choices | Choice available | Process credit card |
| Display choices | Choice unavailable | Display choices |
| Display choices | Cancel | Idle |
| Process credit card | Card valid | Dispense cupcake |
| Process credit card | Card invalid | Process credit card |
| Dispense cupcake | Cupcake taken | Idle |
| Dispense cupcake | Cupcake remains | Dispense cupcake |
State Machines in Photon 2
- In order to implement this in our firmware, what elements / functions do we need to create?
- inputs
- outputs
- state
- state transition logic
- How could we implement these in firmware?
State Machines in Photon 2
-
inputs (e.g.
millis()timer,digitalRead,analogRead) -
outputs (e.g. LED, speaker, OLED screen)
-
state (create
enumto track current state and next state) -
state transition logic
- typically a function with conditional logic like
switchorif - use current state and any input to determine the next state
- typically a function with conditional logic like
State Transition Logic Example
- Let’s look at just one piece of the Sprinkles vending machine, namely processing valid and invalid credit cards
| State | Input | Next State |
|---|---|---|
| Process credit card | Card valid | Dispense cupcake |
| Process credit card | Card invalid | Process credit card |
State Transition Logic Example
- Input: credit card valid or invalid
- global variable
bool cardValid
- global variable
- States: describe all possible states and track current state
enum State {...}State currentState;//Global variables bool cardValid; //is customer card valid enum State {IDLE, DISPLAY, PROCESS, DISPENSE }; //all possible states State currentState; //state the machine is in right now
State Transition Logic Example
- State transition: conditional logic to move to next state based on
currentStateandcardValidvoid updateNextState() { switch(currentState) { case PROCESS: //current state is processing credit card if (cardValid == true) { //credit cart is valid so start dispensing currentState = DISPENSE; } //if cardValid == false, remain in PROCESS state //no else block is needed } }
Credits
- Bill Siever - CS132 FSM (Washington University at St. Louis)
- Bill Siever - CS132 Delta Timing (Washington University at St. Louis)
- USC EE109 State Machines
- Photo by Laurie Parke
- Photo by Michael Olsen</a> on Unsplash
- Photo by Free To Use Sounds on Unsplash
- Photo by NON on Unsplash